Intro
- Today, I'm attempting to dockerize a Laravel and PHP project.
- The goal: run the entire app using only Docker containers.
- I have zero Laravel or PHP installed on my machine, and honestly, zero experience with them.
- Why? To prove that Docker can handle any tech stack, keeping my machine clean.
- I'll document every step here.
For context, setting up Laravel and PHP locally is... a lot. Unlike Node.js where you just install Node and run npm start, PHP requires the language, a package manager (Composer), a web server (Apache or Nginx), and a database (MySQL/PostgreSQL). Dockerizing this saves me from that installation headache.
What's so special about Laravel and PHP?
- Exploring the Laravel docs reveals a laundry list of requirements.
- PHP alone isn't enough.
- Unlike Node.js, which handles the code, runtime, and server logic all in one, PHP needs a separate web server to handle incoming requests.
- This server then pokes the PHP interpreter to run the code.
- Setting this up locally, along with a database, can be quite annoying.
Target Setup
- Source Code: A folder on the host machine containing the Laravel app.
- PHP Container: Has the PHP interpreter and access to the source code.
- Nginx Container: The web server. It takes requests and forwards them to the PHP container.
- MySQL Container: Stores our data.
- Connectivity: The PHP container needs to talk to the MySQL container.
These form our 3 Application Containers.
Utility Containers
Laravel needs tools to function:
- Composer: The PHP package manager (think npm for PHP).
- Artisan: Laravel's command-line tool for tasks like database migrations.
- NPM: Yes, even Laravel uses it for some frontend logic.
Overall
We need 6 containers in total:
- 3 Application: PHP, Nginx, MySQL
- 3 Utility: Composer, Artisan, NPM
Let's Start Dockerizing
Prerequisites
Make sure you have Docker and Docker Compose installed. Follow the official docs if you haven't.
Step 1: Create docker-compose.yaml
We'll declare our 6 services here.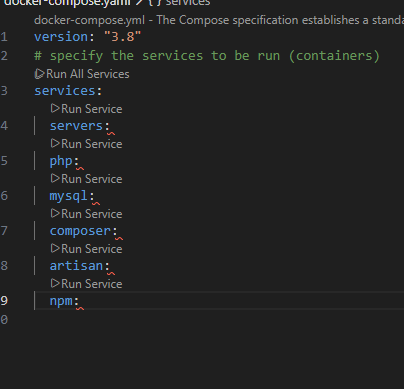
Server Container (Nginx)
We'll use the official Alpine image and expose port 8000.
server:
image: 'nginx:stable-alpine'
ports:
- "8000:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:ro- Explanation: We map port 8000 on the host to port 80 in the container. We also mount our local config file.
Create nginx/nginx.conf on the host:
server {
listen 80;
index index.php index.html;
server_name localhost;
root /var/www/html/public;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass php:3000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
}- Explanation: We set the root to
/var/www/html/public(Laravel's entry point). It listens on port 80 and forwards.phprequests to thephpcontainer on port 3000.
PHP Container
We need a custom image to install specific PHP extensions required by Laravel.
Create dockerfiles/php.dockerfile:
FROM php:7.4-fpm-alpine
WORKDIR /var/www/html
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql- Explanation: Based on PHP 7.4 FPM Alpine. We install
pdoandpdo_mysqlfor database connectivity. NoENTRYPOINTis needed; it defaults tophp-fpm.
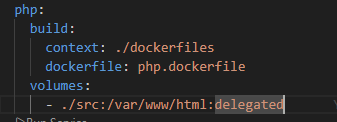
Update docker-compose.yaml:
php:
build:
context: ./dockerfiles
dockerfile: php.dockerfile
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/html:delegated- Explanation: We build from our custom Dockerfile and bind mount the
./srcfolder so the container can see our code. Note: PHP-FPM usually listens on port 9000. If we want it on 3000 (as referenced in Nginx config), we'd need to configure that, or just update Nginx to point to 9000. Let's assume we update Nginx:
fastcgi_pass php:9000;
MySQL Container
Standard setup using the official image.
mysql:
image: 'mysql:5.7'
env_file:
- ./env/mysql.envComposer Container
We need a custom image to run Composer commands.
FROM composer:latest
WORKDIR /var/www/html
ENTRYPOINT [ "composer", "--ignore-platform-reqs" ]- Explanation: Uses the latest Composer image. The entrypoint runs
composerignoring platform requirements (since we're in a container).
Add to docker-compose.yaml:
composer:
build:
context: ./dockerfiles
dockerfile: composer.dockerfile
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/html:delegatedCreate a Laravel App
Run the composer container to scaffold the app:
docker-compose run --rm composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel .- Explanation: This runs
create-projectinside the container, depositing the files into./srcon your host.
Running the App
Check src/.env for database config and update it to match your MySQL container settings:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=mysql
DB_PORT=3306
...Ensure the Nginx container also sees the source code:
server:
# ... other config
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/html:delegated
- ./nginx/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:roSpin it up:
docker-compose up -d server php mysqlVisit http://localhost:8000.
Encountered Issues & Fixes
I hit a permission error: file_put_contents(...): Failed to open stream: Permission denied.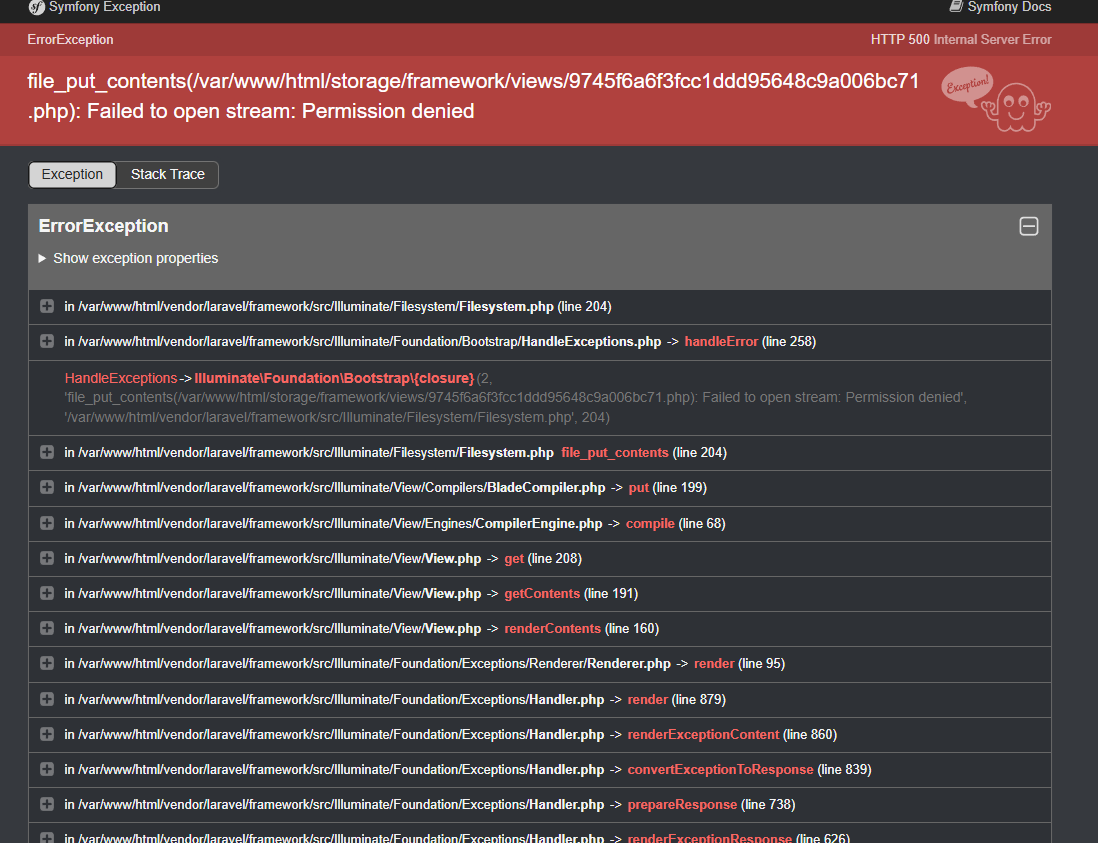
This happens because the container user doesn't have write permissions to the bind-mounted folders on Linux/WSL. Also, Laravel 12+ requires PHP 8.4.
The Fix:
Update dockerfiles/php.dockerfile to handle permissions and use a newer PHP version:
FROM php:8.4-fpm-alpine
WORKDIR /var/www/html
COPY src .
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql
# Create a user 'laravel' to match the host user ID (often 1000)
RUN addgroup -g 1000 laravel && adduser -G laravel -g laravel -s /bin/sh -D laravel
USER laravelUpdate dockerfiles/composer.dockerfile similarly:
FROM composer:latest
RUN addgroup -g 1000 laravel && adduser -G laravel -g laravel -s /bin/sh -D laravel
USER laravel
WORKDIR /var/www/html
# Switch to root if needed for specific ops, but default to laravel
# USER root
ENTRYPOINT [ "composer", "--ignore-platform-reqs" ]Finally, run migrations using the PHP container (or a dedicated artisan container):
docker-compose exec php php artisan migrateWorking App
Success!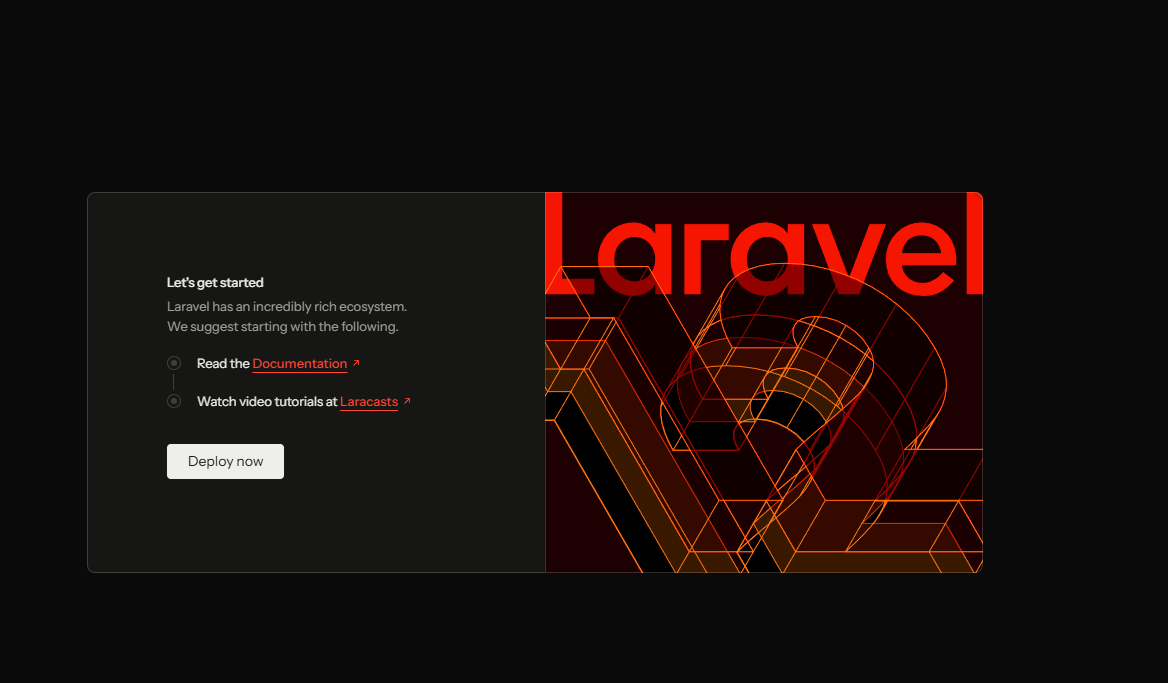
I changed src/resources/views/welcome.blade.php and the changes reflected instantly.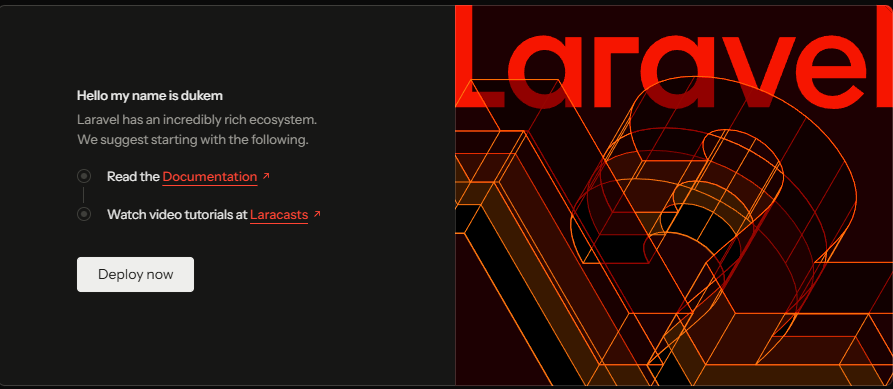
Artisan Container
We can reuse the php.dockerfile for Artisan commands.
artisan:
build:
context: ./dockerfiles
dockerfile: php.dockerfile
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/html
entrypoint: ["php", "/var/www/html/artisan"]NPM Container
Simple setup for frontend assets.
npm:
image: 'node:18-alpine'
working_dir: /var/www/html
entrypoint: ["npm"]
volumes:
- ./src:/var/www/htmlBind Mounts vs. Copy
- Bind Mounts: Great for development. Changes on your host are instantly seen in the container.
- Copy: Better for production. You bake the code into the image.
For a production-like Nginx image (dockerfiles/nginx.dockerfile):
FROM nginx:stable-alpine
WORKDIR /etc/nginx/conf.d
COPY nginx/nginx.conf .
RUN mv nginx.conf default.conf
WORKDIR /var/www/html
COPY src .Update docker-compose.yaml to build it:
server:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: dockerfiles/nginx.dockerfile
ports:
- "8080:80"
depends_on:
- php
- mysql